|
Light harvesting and light extraction |
|||||
High-efficiency photo-electron conversion devices Semiconductor processes and nanofabrication Characterizations and applications of nanomaterials Optical characterization of graphene Graphene-gold oxide photodetector Optical analysis of hollow gold nanoparticles Photomodification of hollow gold nanoparticles for high-density data storage Light harvesting and light extraction Light extraction efficiency of LEDs Antireflection structures for solar cells Optical analysis techniques Eco-friendly devices and sensors
|
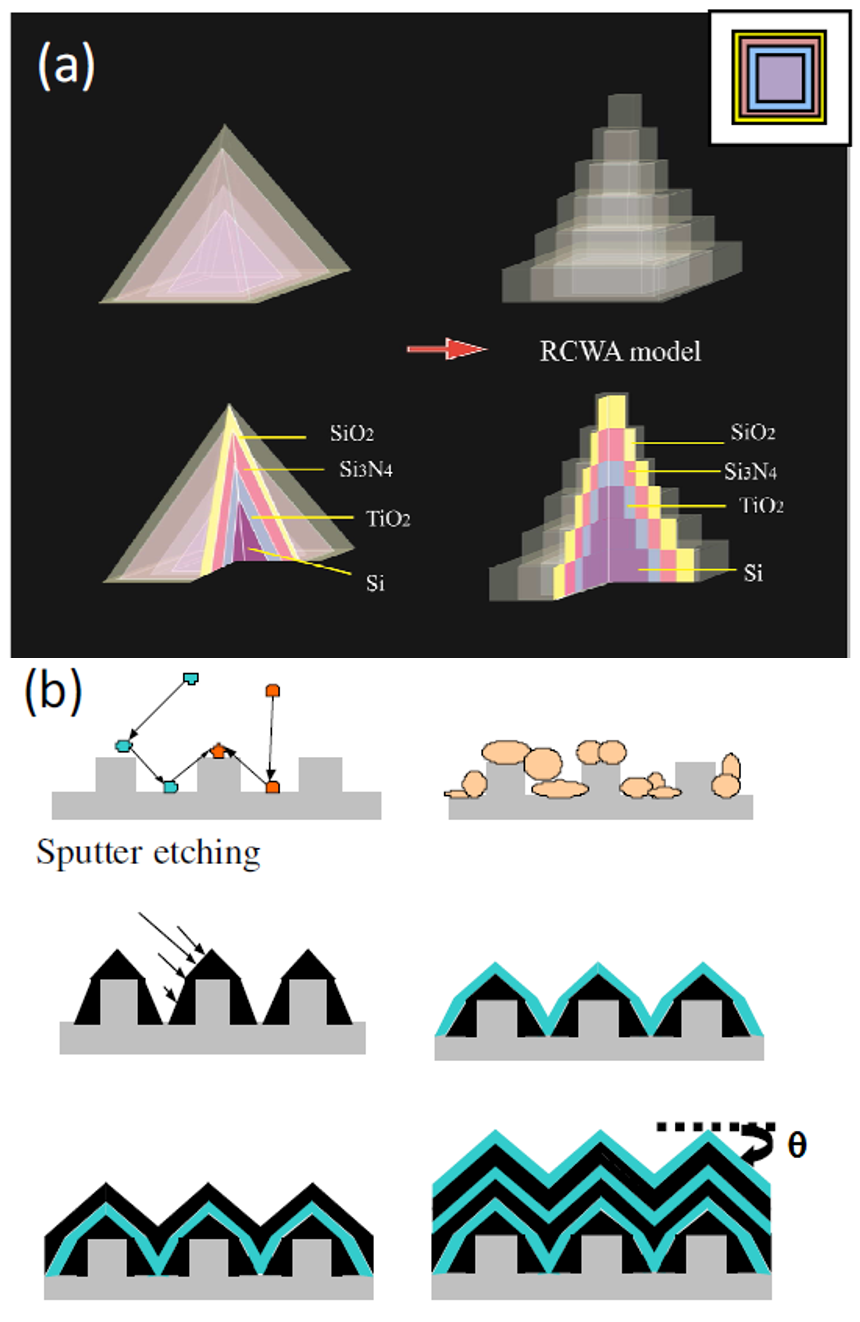
Using autocloning effects to develop broadbandwidth, omnidirectional antireflection structures for silicon solar cells In this study, we used the autocloning effect on pyramid structures to develop broad-bandwidth, omnidirectional antireflection structures for silicon solar cells. The angular dependence of reflectance on several pyramid structures was systematically investigated. The deposition of three-layer autocloned films reduced the refractive index gap between air and silicon, resulting in an increase in the amount of transmitted light and a decrease in the total light escaping. The average reflectance decreased dramatically to ca. 2–3% at incident angles from 0 to 60° for both subwavelength– and micrometer–scale pyramid structures. The measured reflectance of the autocloned structure was less than 4% in the wavelength range from 400 to 1000 nm for incident angles from 0 to 60°. Therefore, the autocloning technique, combined with optical thin films and optical gradient structures, is a practical and compatible method for the fabrication of broadbandwidth, omnidirectional antireflection structures on silicon solar cells. |
Schematic representation of the autocloning technique. (a) Geometric setup of the
|
|||
Copyright(c) 2008 Nano-optpelectronics Lab., Department of Material Science and Engineering, National Taiwan University No. 1, Sec. 4, Roosevelt Road, Taipei, 10617 Taiwan(R.O.C) Phone:+886-2-3366-3240 Fax:+886-2-2362-7651 |
|||||